SPI means Serial Peripheral Interface.
The Serial Peripheral Interface Bus or SPI bus is a synchronous serial data link de facto standard, named by Motorola, that operates in full duplex mode. Devices communicate in master/slave mode where the master device initiates the data frame. Multiple slave devices are allowed with individual slave select (chip select) lines. Sometimes SPI is called a four-wire serial bus, contrasting with three-, two-, and one-wire serial buses. SPI is often referred to as SSI (Synchronous Serial Interface).
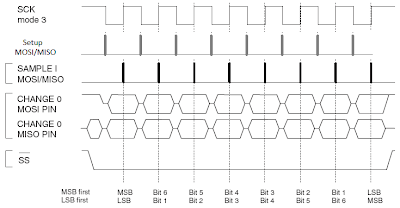
The SPI Mode 3 waveform is
We have seen the working of SPI and the SPI Master in the previous page. Now let us see about the SPI Slave.Click here to goto SPI MASTER Page.
SPI SLAVE VERILOG MODULE:
The slave module is simple. It is just like a shift register with additional control signal SS_bar. The data is sampled in at positive edge of SCK and shifted out at negative edge of SCK. The data transmission of slave is active only when SS_bar input signal is low, otherwise it is disconnected from the bus & Sdout is tri-stated. Other control signals are similar to that of SPI Master Module.
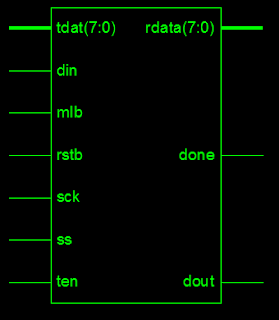
SPI Slave Block Diagram is
The SPI Slave module verilog code is as follows:
//read from sdin
always @(posedge sck or negedge rstb)
begin
if (rstb==0)
begin rreg = 8'h00; rdata = 8'h00; done = 0; nb = 0; end //
else if (!ss) begin
if(mlb==0)
begin rreg ={sdin,rreg[7:1]}; end
else
begin rreg ={rreg[6:0],sdin}; end
nb=nb+1;
if(nb!=8) done=0;
else begin rdata=rreg; done=1; nb=0; end
end
end
//send to sdout
always @(negedge sck or negedge rstb)
begin
if (rstb==0)
begin treg = 8'hFF; end
else begin
if(!ss) begin
if(nb==0) treg=tdata;
else begin
if(mlb==0)
begin treg = {1'b1,treg[7:1]}; end
else
begin treg = {treg[6:0],1'b1}; end
end
end //!ss
end //rstb
end //always
//read from sdin
always @(posedge sck or negedge rstb)
begin
if (rstb==0)
begin rreg = 8'h00; rdata = 8'h00; done = 0; nb = 0; end //
else if (!ss) begin
if(mlb==0)
begin rreg ={sdin,rreg[7:1]}; end
else
begin rreg ={rreg[6:0],sdin}; end
nb=nb+1;
if(nb!=8) done=0;
else begin rdata=rreg; done=1; nb=0; end
end
end
//send to sdout
always @(negedge sck or negedge rstb)
begin
if (rstb==0)
begin treg = 8'hFF; end
else begin
if(!ss) begin
if(nb==0) treg=tdata;
else begin
if(mlb==0)
begin treg = {1'b1,treg[7:1]}; end
else
begin treg = {treg[6:0],1'b1}; end
end
end //!ss
end //rstb
end //always









Hey What s the significance of "tdat" in Slave module... i'm not getting... can you explain me abt tat plz....
ReplyDeleteVery nice tutorial, but I was wondering where is the link for spi slave, master and test-bench. The link provided is broken.
ReplyDeleteelazığ
ReplyDeletebilecik
kilis
sakarya
yozgat
JİEPS
https://titandijital.com.tr/
ReplyDeletediyarbakır parça eşya taşıma
nevşehir parça eşya taşıma
bolu parça eşya taşıma
batman parça eşya taşıma
VGSV2
kırşehir evden eve nakliyat
ReplyDeletegiresun evden eve nakliyat
tekirdağ evden eve nakliyat
ardahan evden eve nakliyat
izmir evden eve nakliyat
7KEXC
C20DD
ReplyDeleteTokat Şehir İçi Nakliyat
Afyon Evden Eve Nakliyat
Edirne Evden Eve Nakliyat
Gümüşhane Evden Eve Nakliyat
Sinop Parça Eşya Taşıma
Hakkari Şehirler Arası Nakliyat
Çorum Şehirler Arası Nakliyat
Elazığ Şehirler Arası Nakliyat
Sivas Şehir İçi Nakliyat
AF073
ReplyDeletebkex
kredi kartı ile kripto para alma
papaya
binance ne demek
okex
binance
telegram en iyi kripto grupları
bitexen
telegram türk kripto kanalları
79925
ReplyDeletekripto para haram mı
bybit
bitcoin nasıl oynanır
gate io
binance referans kodu
binance referans kod
bybit
kripto para nasıl alınır
kraken
A0B537B014
ReplyDeleteperformans arttırıcı
sildegra
cobra vega
kaldırıcı
yapay kızlık zarı
themra macun
bayan azdırıcı damla
fx15
viagra
65F10C1F4E
ReplyDeletegörüntülü şov whatsapp numarası
geciktirici
skype şov
kaldırıcı
bufalo içecek
görüntülü show
lady era
viga
maxman
B230F6F48E
ReplyDeletenovagra hap
degra 100 mg
bayan azdırıcı damla
viga
viagra
cobra vega
yapay kızlık zarı
telegram show
stag
vodiskpreukaznaslovensku
ReplyDeleteZákonný vodičský preukaz | jazdiť legálne na Slovensku
Integrita vodičského preukazu získaného z jednoduchého vodičského preukazu zostala vždy neporušená. Preto implementujeme prísne
06577A9A45
ReplyDeleteinstagram bot takipci
This is a very helpful explanation of SPI Slave functionality.
ReplyDelete210E722E6A
ReplyDeleteTelegram Mining Botları
Telegram Güvenilir Coin Botları
Telegram Para Kazanma
Telegram Para Kazanma
Coin Botları
96171F0BAA
ReplyDeleteucuz tiktok takipçi
instagram beğeni satın al
kaliteli takipçi
mobil ödeme takipçi
bayan takipçi
9E7EF5A6A2
ReplyDeletemmorpg oyunlar
sms onay
mobil ödeme bozdurma
en iyi takipci satin alma sitesi
-
24EF7DBC1A
ReplyDeleteİnternet üzerinde popüler videoların izlenme sayılarını artırmak isteyen bazı kullanıcılar, çeşitli yöntemler denemektedir. Özellikle "shorts izlenme hilesi" gibi ifadelerle arama motorlarında karşılaşmak mümkündür. Ancak, bu tür hilelerin kullanımı hesabınızın güvenliğini tehlikeye atabilir ve platform kurallarına aykırıdır. Daha güvenli ve sürdürülebilir bir başarı için organik büyüme yollarını tercih etmek her zaman daha doğru olacaktır.
Sosyal medya hesaplarınızı büyütmek için çeşitli yöntemler denemek isteyebilirsiniz. Ancak, bazen zaman ve emek gerektiren bu süreçte, facebook takipçi hilesi gibi kısa yolları araştırmak da cazip gelebilir. Bu tür uygulamaların güvenilirliği ve sonuçları hakkında dikkatli olmak önemlidir. Unutmayın, organik büyüme her zaman daha kalıcı ve etkilidir.
İnternet üzerinde içerik üretirken, videolarınızı daha geniş kitlelere ulaştırmak için çeşitli yöntemler kullanabilirsiniz. Özellikle TikTok'ta popüler olmak ve videolarınızı kaydetmek istediğinizde, bu konuda yardımcı olabilecek hizmetler de mevcuttur. Eğer siz de hızlıca TikTok kaydetme işlemini gerçekleştirmek veya bu konuda destek almak istiyorsanız, detaylar için tiktok kaydetme hizmetlerinden faydalanabilirsiniz. Bu sayede içeriklerinizi daha etkin bir şekilde yönetebilirsiniz.
Sosyal medya hesaplarınızın görünürlüğünü artırmak için çeşitli yöntemler deneyebilirsiniz. Örneğin, daha fazla etkileşim ve takipçi kazanmak için bazı kişiler **twitter izlenme satın al** seçeneğini tercih edebiliyor. Bu sayede, profilinizin popülerliği kısa sürede artarken, daha geniş kitlelere ulaşmanız mümkün oluyor. Ancak, bu tür yöntemlerin dikkatli ve bilinçli kullanılması önemlidir.
Sosyal medya hesaplarınızı büyütmek için birçok farklı yöntem deniyorsanız, bazen dikkat çekici ve hızlı sonuçlar sağlayan çözümler arayabilirsiniz. Örneğin, pinterest takipçi hilesi gibi hizmetler, hesabınızın görünürlüğünü artırmaya yardımcı olabilir. Ancak, bu tür yöntemlerin kalıcı ve güvenilir olup olmadığını dikkatlice değerlendirmeniz önemlidir. Doğru stratejilerle organik büyüme sağlamak her zaman daha sağlıklıdır.
Instagram izlenme hilesi, içeriklerin daha fazla kişiye ulaşmasını sağlayarak takipçi sayısını artırmada etkili bir yöntem olabilir. Bu konuda birçok kişi, daha hızlı sonuç almak için çeşitli sitelerden yardım almayı tercih ediyor. Örneğin, [instagram izlenme hilesi](https://begenisatinal.com.tr/8972/instagram-izlenme-hilesi) gibi bağlantılar, kullanıcıların taleplerine uygun çözümler sunabiliyor. Ancak, bu tür uygulamaların güvenilirliği ve etik olup olmadığı konusunda dikkatli olmak gerekir.
YouTube izlenme sayınızı artırmak istiyorsanız, çeşitli yöntemler ve stratejiler deneyebilirsiniz. Bu süreçte, güvenilir ve kaliteli hizmetler sunan platformlardan destek almak önemlidir. Örneğin, youtube izlenme satın alarak videolarınızın görünürlüğünü hızla artırabilirsiniz. Böylece, daha fazla izleyiciye ulaşma şansınız yükselir ve kanalınızın büyümesine katkıda bulunur.